The Changing Landscape of South African Cross-Border Payments
South Africa plays a crucial role in Africa's financial landscape, with significant sums of money constantly flowing across its borders. Traditionally, these cross-border payments relied heavily on bank transfers, a process that is often slow, costly, and complicated.
However, this landscape is evolving. New payment options are emerging and changing the way South Africans send and receive money internationally. This begs the question: what factors are driving this change, and how are they impacting the South African economy?
Major Payment Corridors and Driving Forces
South Africa's cross-border payment activity is largely focused on key corridors. These connect with neighboring countries like Zimbabwe and Mozambique, along with major international trade partners.
Two primary forces shape these corridors: economic opportunities and migrant worker remittances. Trade with neighboring countries, for example, creates a constant stream of business transactions that demand efficient payment systems.
Many South Africans work abroad and send money home to their families. This underscores the need for accessible and cost-effective cross-border payment options. This interconnectedness further emphasizes the importance of streamlined systems.
Navigating the Complexities and Hidden Costs
Businesses and migrant workers face considerable challenges when making cross-border payments. These challenges include fluctuating exchange rates, varying fees, and complex regulations. These often unforeseen hidden costs can have a substantial impact on the final amount received.
The need for greater transparency in the cross-border payment process is clear. This transparency would allow individuals and businesses to make informed decisions about the best way to send and receive money internationally.
Addressing Cross-Border Payment Challenges
Cross-border payments within South Africa and the wider sub-Saharan Africa region are a key focus for financial institutions and regulatory bodies. The G20 Roadmap for Enhancing Cross-border Payments aims to tackle challenges like high costs, slow transaction speeds, and limited access.
This roadmap includes 19 building blocks designed to make cross-border payments cheaper, faster, more transparent, and more accessible. In February 2025, South African Reserve Bank Governor Lesetja Kganyago highlighted the need for greater interoperability and regulatory alignment within the region.
He suggested that learning from solutions implemented in other regions could improve cross-border payments in sub-Saharan Africa. The international community is working to address these issues, with the Financial Stability Board expected to deliver a progress report in October 2025. You can learn more about this at the South African Reserve Bank.
The Role of Financial Institutions
Understanding which institutions dominate South Africa's cross-border payment market is essential. Traditional banks still maintain a significant market share. However, new players, such as fintech companies, are rapidly gaining traction.
These newcomers offer innovative solutions like mobile money and online platforms, which are often faster and less expensive than traditional methods. This competition is transforming the market and driving innovation, ultimately benefiting both consumers and businesses. This evolving landscape sets the stage for a more dynamic and accessible future for cross-border payments in South Africa.
Digital Revolution: How Tech Is Transforming Money Movement

The way South Africans send and receive money across borders is evolving. Gone are the days of long queues at traditional banks. Digital solutions, like smartphone apps and online platforms, are increasingly popular for cross-border payments in South Africa, providing a faster and more convenient option.
This shift towards digital platforms is not uniform across South Africa. Urban professionals, with easy internet access, are leading the charge in adopting these technologies. However, mobile money solutions are also gaining momentum in rural areas, even with less consistent connectivity. This expanding accessibility is crucial for boosting financial inclusion throughout the country.
Digital Adoption Across South Africa
Fintech companies are actively working to resolve the difficulties associated with traditional cross-border payments. They are tackling issues like high fees, opaque exchange rates, and frustrating processing times. Some platforms utilize blockchain technology to expedite transactions and reduce costs. Many also provide transparent, real-time exchange rates, enhancing the overall user experience and driving the adoption of digital solutions.
The following table highlights the key differences between digital and traditional remittance methods in South Africa.
To better understand these contrasting approaches, let's compare digital and traditional methods side-by-side. This table outlines the key factors South Africans should consider when choosing a cross-border payment method.
| Feature | Digital Methods | Traditional Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Typically within minutes or hours | Can take several days |
| Cost | Generally lower transaction fees | Often higher fees, including SWIFT charges |
| Convenience | Accessible 24/7 via apps and online platforms | Requires visiting a physical branch during business hours |
| Transparency | Real-time exchange rates and transaction tracking | Less transparent fees and exchange rates |
| Security | Secure platforms with encryption and fraud protection | Potential vulnerabilities to fraud and errors |
| Accessibility | Increasingly available, even in remote areas via mobile money | Limited access in areas with fewer bank branches |
This comparison reveals the advantages digital methods offer in terms of speed, cost, and convenience. However, it's crucial to choose reputable platforms with strong security measures.
The Growth of Digital Remittances
Digital remittance services are experiencing significant growth in South Africa. The transaction value in the Digital Remittances market is projected to reach US$513.44 million by 2025. This underscores the substantial demand for these solutions. This growth is part of a wider trend across Africa, where the digital payments ecosystem is expanding rapidly. Find more detailed statistics here.
The Key to Success
While the potential of digital solutions is clear, not every platform succeeds. The platforms that prioritize user-friendliness, robust security, and affordability tend to perform better. Understanding user needs and providing practical solutions are essential for thriving in this competitive market. The ongoing evolution of digital cross-border payments offers a more inclusive and efficient financial future for millions of South Africans.
Navigating The Regulatory Maze Of International Transfers

Behind every cross-border payment from South Africa lies a network of regulations. These regulations, designed to protect the financial system, can be complex for both individuals and businesses to understand. Knowing these regulations is essential for smooth and compliant international transfers.
The South African Reserve Bank (SARB) and Exchange Control
The South African Reserve Bank (SARB) plays a vital role in regulating cross-border payments from South Africa. It enforces exchange control regulations, which determine how much money can be transferred into and out of the country. These limits depend on the transfer's purpose, such as supporting family members or paying for imported goods.
South African residents have an annual individual discretionary allowance of R1 million. This allowance permits them to transfer funds abroad for various reasons, including gifts, travel, and investments, without needing prior approval from the SARB.
The Financial Intelligence Centre Act (FICA)
In addition to exchange control, the Financial Intelligence Centre Act (FICA) aims to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing. This act requires financial institutions to verify their customers’ identities.
This Know Your Customer (KYC) process involves submitting identification documents and proof of residence. Although this process may seem inconvenient, it’s a crucial step in ensuring the financial system’s security and integrity. The increasing use of technology for cross-border payments in South Africa reflects global trends. For instance, see how changes in technology are impacting systems internationally, such as the IRS.
Documentation and Compliance
Navigating regulatory requirements often involves specific documentation. For example, businesses making cross-border payments might need to submit invoices, contracts, or other supporting documents to prove their transactions’ legitimacy. This ensures compliance and helps avoid delays or penalties.
Understanding the reporting thresholds for certain transactions is also important for businesses involved in larger international transfers.
Recent Regulatory Shifts
South Africa's regulatory landscape is constantly changing. Recent changes seek to balance security concerns with the need for efficient cross-border payments. These changes highlight the importance of technology to streamline compliance processes and improve transparency. Staying informed about regulatory updates is essential for businesses and individuals involved in international transfers. This awareness allows for better planning and facilitates smoother transactions.
The True Cost Revealed: What You’re Really Paying
The advertised fee for sending money abroad from South Africa doesn’t always reflect the complete picture. This section unveils the actual costs associated with cross-border payments, examining hidden fees and exchange rate markups that can significantly impact the amount your recipient ultimately receives.
Decoding Fee Structures and Exchange Rate Markups
Understanding KYC (Know Your Customer) and Anti-Money Laundering procedures is essential for cross-border transactions. For further details on this crucial subject, refer to this informative resource on KYC and Anti-Money Laundering. Banks frequently add a margin to the mid-market exchange rate, essentially generating profit from the currency conversion.
This markup can be substantial, particularly for less common currencies. Digital platforms often promote lower fees, yet some still incorporate markups into their exchange rates. Traditional money transfer operators may also have intricate fee structures that can be challenging to understand.
Comparing the total cost, inclusive of all fees and markups, is crucial for selecting the most economical option.
Comparing Costs Across Providers
Consider a practical scenario: sending R10,000 to the UK. One bank might impose a flat fee of R250 in addition to a 2% markup on the exchange rate. A digital platform might advertise no fees but apply an exchange rate 3% above the mid-market rate.
A money transfer operator might offer a competitive exchange rate while charging a substantial transfer fee. The discrepancies can be considerable. When transferring funds to Zimbabwe or China, the cost variations between providers can be even greater, sometimes amounting to hundreds of rands. Selecting the wrong provider could significantly reduce the funds your recipient actually receives.
The following table provides a comparative analysis of costs associated with cross-border payments from South Africa.
Cross Border Payment Costs in South Africa Comparative analysis of fees, exchange rates, and transfer times across major service providers in South Africa
| Service Provider | Transfer Fee (R) | Exchange Rate Markup | Transfer Time | Maximum Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Example Bank A | 250 | 2% | 2-3 Business Days | R1,000,000 |
| Example Digital Platform B | 0 | 3% | 1 Business Day | R500,000 |
| Example Money Transfer Operator C | 500 | 1% | 24 Hours | R250,000 |
This table uses example data for illustrative purposes. Actual fees and rates will vary depending on the specific provider and transfer details.
As the table illustrates, even with no upfront transfer fee, a higher exchange rate markup can result in a larger overall cost. It's crucial to compare both the stated fees and the exchange rate offered to determine the true cost of your transfer.
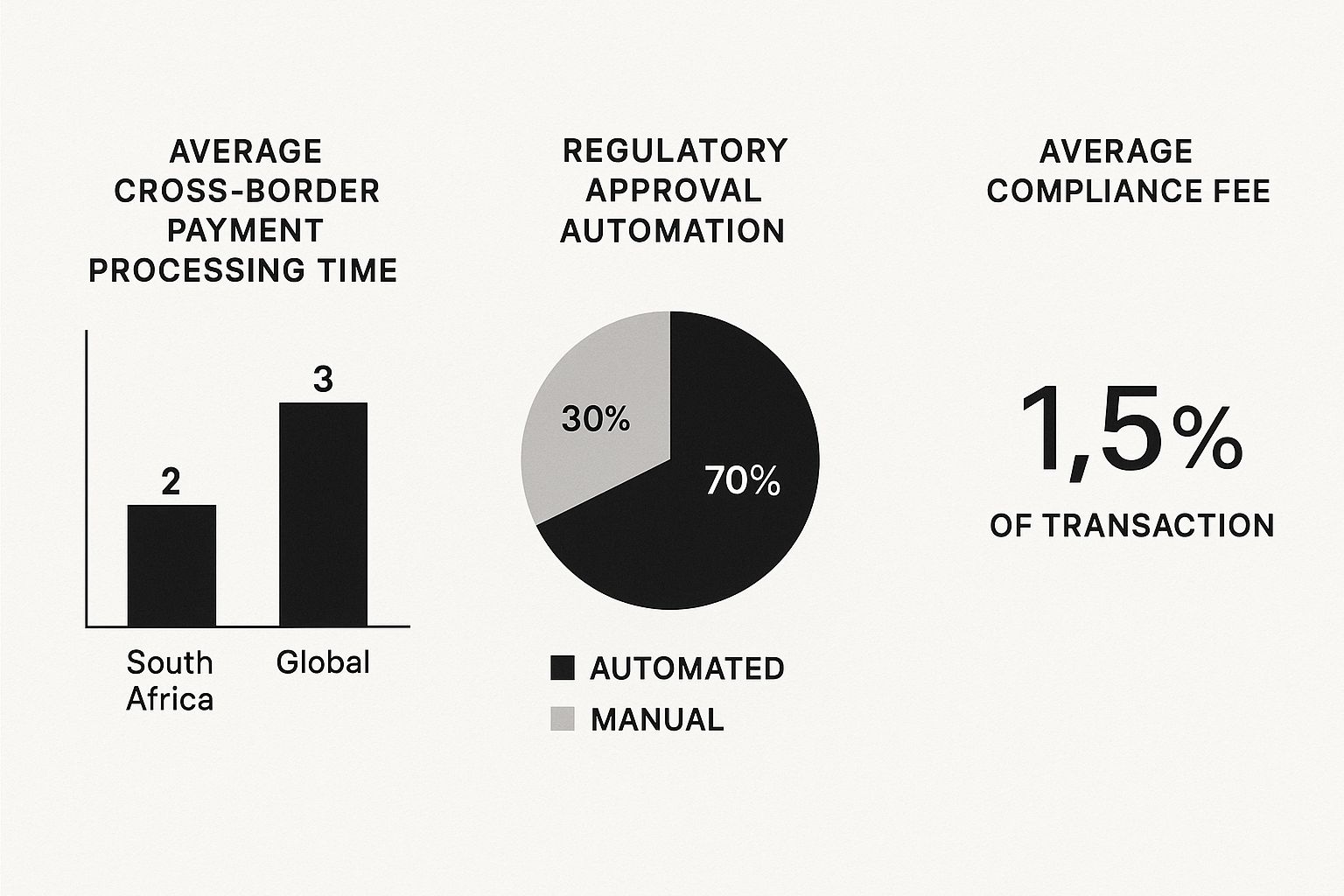
As the infographic demonstrates, South Africa processes payments more quickly than the global average, boasting a high degree of regulatory automation. However, the average compliance fee of 1.5% remains a pertinent factor.
Tips for Minimizing Transfer Costs
Resourceful South Africans utilize various strategies to minimize cross-border payment expenses. Comparing exchange rates from multiple providers, including banks and digital platforms, is essential. Strategically timing your transfer can also be advantageous, as exchange rates are subject to constant fluctuation.
Sending larger sums less frequently can often lessen the impact of fixed fees. Prioritizing providers that offer transparent fee structures and utilize the mid-market exchange rate, or a rate very close to it, is vital. These tactics can lead to substantial savings over time.
Business Without Borders: Optimizing Global Transactions
For South African businesses involved in international trade, efficient cross-border payments are vital for success. This section explores the challenges and opportunities these businesses encounter when managing international transactions. We’ll examine strategies for managing foreign currency risk, optimizing payment timing, and choosing the right payment systems.
Managing Foreign Currency Exposure
Fluctuations in exchange rates can significantly impact a business's profits. A sudden weakening of the Rand, for example, could increase the cost of imported goods, reducing profit margins. This is why effective foreign currency management is so important.
One strategy is using forward contracts. Forward contracts allow businesses to lock in an exchange rate for a future transaction, providing greater cost certainty. Another approach is to maintain multi-currency accounts. This allows businesses to hold funds in different currencies, mitigating the risk of adverse exchange rate movements.
Businesses can then strategically manage their currency holdings to take advantage of favorable exchange rates. These proactive measures help South African businesses protect themselves from the inherent volatility of the foreign exchange market. This, in turn, leads to more stable and predictable financial performance.
Optimizing Payment Timing and Infrastructure
Timing is critical in international trade. Delayed payments can strain supplier relationships and disrupt supply chains. Conversely, paying too early can tie up valuable working capital.
Optimizing payment timing requires careful coordination with suppliers and customers. This might involve negotiating favorable payment terms or implementing automated payment systems.
Choosing the right payment infrastructure is also essential. Businesses need solutions that are fast, reliable, and cost-effective. Traditional bank transfers can be slow and expensive, particularly for smaller transactions. Fintech platforms, like Zaro, offer faster and more affordable solutions for cross border payments south africa, leveraging real exchange rates and eliminating SWIFT fees.
Case Studies and Practical Approaches
South African companies, from tech startups to established exporters, are adopting innovative payment practices. Some businesses are using platforms like Zaro to make instant payments to suppliers in other African countries, bypassing the delays and high costs of traditional banking systems.
This allows them to strengthen supplier relationships and improve supply chain efficiency. Other businesses are using multi-currency accounts to manage their global payroll, simplifying payments to international contractors and employees. These practical examples demonstrate the tangible benefits of optimizing global transactions.
Setting Up International Business Accounts
Setting up international business accounts can streamline global transactions and offer numerous benefits. With accounts in major trading currencies like USD, businesses can receive payments directly from international customers, reducing reliance on costly intermediary banks.
These accounts also make it easier to pay international suppliers in their local currencies, potentially strengthening business relationships and improving negotiation power.
Negotiating with Payment Providers and Selecting the Right Solutions
Negotiating favorable terms with payment providers is vital. Businesses should compare fees, exchange rates, and transfer times across various providers, including banks, digital platforms, and specialized transfer services.
The best solution depends on the business's specific needs and target markets. For example, a business trading frequently with countries in sub-Saharan Africa might benefit from a payment platform specializing in regional transactions, such as the Pan-African Payment and Settlement System. These strategic choices help South African businesses unlock further growth in the international market.
Beyond Transfers: The Economic Impact of Money in Motion
Cross-border payments are more than simple transactions; they are vital connections linking South Africa to the global economy. Efficient cross-border payment systems are a catalyst for economic development, strengthening South Africa's global standing. Improvements in these systems can significantly benefit the nation's overall economy.
The Ripple Effect of Remittances
Remittances, money sent home by South Africans working abroad, have a profound impact. These funds are often critical for families and communities, especially in areas dependent on income from overseas workers. This income boosts household spending, supports local businesses, and can even drive investment in crucial sectors like education and healthcare. For instance, remittances may enable families to invest in their children's education, ultimately building a more skilled workforce and a stronger national economy.
Payment Infrastructure and Economic Growth
Payment infrastructure significantly influences trade volumes, foreign investment, and entrepreneurial activities. Efficient systems reduce transaction costs and processing times, simplifying international trade for South African businesses. This, in turn, attracts foreign investment, as businesses view South Africa as a reliable trading partner. Streamlined payment processes also empower local entrepreneurs by facilitating access to global markets, enabling greater participation in the international economy.
Emerging Trends and New Opportunities
The payments landscape is continuously changing, and South Africa is keeping pace. Emerging trends, particularly in digital payments and the subscription economy, are creating new business models and opportunities. The rise of the subscription economy, a global trend, is having a substantial impact locally. South Africa has over 7 million active subscriptions, valuing its subscription economy at US$530 million, with projections exceeding US$800 million by 2025. This reflects the global trend, with the worldwide subscription economy predicted to reach US$1.5 trillion by 2025, up from US$650 billion in 2020. Cross-border payments are crucial for supporting this growth, enabling international subscriptions and trade. Explore this topic further. This interconnectedness underscores the need for efficient cross-border payment systems to support these expanding sectors. Consider a South African entrepreneur launching a software-as-a-service platform and seamlessly receiving payments from international subscribers thanks to efficient cross-border systems.
Transforming South Africa’s Economic Trajectory
Understanding the broader economic implications of cross-border payments provides valuable insights for South Africa's future. Improved payment capabilities facilitate more than just individual transactions; they can transform the country's economic trajectory. By minimizing friction in international trade and promoting innovation, these enhancements contribute to sustainable economic growth and strengthen South Africa's global competitiveness. Ultimately, this can lead to increased prosperity and opportunities for all South Africans.
The Future of Money Movement: What's Next for South Africa
The cross-border payment landscape in South Africa is constantly changing. This section explores the technologies and initiatives set to reshape how South Africans send and receive money internationally. We'll look beyond the hype surrounding blockchain and distributed ledger technologies (DLTs), focusing on practical applications for South African businesses and individuals.
Project Khokha and the Future of Payments
The South African Reserve Bank's Project Khokha is a key development. This initiative explores DLTs' potential to improve interbank settlements' efficiency and security. Imagine a system where banks could settle transactions instantly, eliminating delays and reducing costs. This could significantly impact the speed and affordability of cross-border payments in South Africa.
Pan-African Payment and Settlement System (PAPSS)
Regional integration initiatives, like the Pan-African Payment and Settlement System (PAPSS), aim to reduce the cost and increase the speed of intra-African payments. This is crucial for boosting intra-African trade and empowering South African businesses operating across the continent. By simplifying cross-border transactions, PAPSS could unlock significant growth opportunities for South African businesses engaged in regional trade.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) and the Future of Money
Another developing area is the potential introduction of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs). These digital versions of the Rand could interact with existing payment systems in new ways. However, how CBDCs will integrate into the current financial infrastructure remains unclear. There's ongoing debate about the potential benefits and challenges of CBDCs. Further research and development are needed to determine their long-term impact.
Separating Hype from Reality: Technologies to Watch
While many emerging technologies promise to revolutionize payments, it's important to distinguish realistic solutions from hype. Some, like certain blockchain applications, offer real potential for streamlining cross-border payments. Others may not gain traction due to regulatory hurdles or technical limitations. One example is integrating stablecoins into payment systems. While stablecoins could offer a less volatile alternative to traditional currencies, regulatory uncertainties and potential security concerns could hinder their adoption.
Preparing for the Future of Payments
South African businesses and individuals must stay informed and adapt to the changing financial landscape. Understanding these developments is crucial for proactive planning, ensuring you're not caught off guard by disruptive changes. By understanding the market's direction, South Africans can make strategic financial decisions for their future.
Ready to experience the future of cross-border payments? Discover how Zaro can transform your international transactions.
Article created using Outrank
