Decoding South Africa's Export Regulatory Landscape
Navigating South Africa's export regulations can be a complex undertaking. Understanding the intricacies of this system is essential for businesses looking to access international markets. This section outlines the key aspects of South Africa's export regulatory framework, offering practical guidance for businesses aiming to expand globally.
Key Regulatory Bodies and Their Roles
Several institutions are central to the export process in South Africa. The International Trade Administration Commission (ITAC) plays a vital role in regulating trade and managing trade remedies. ITAC investigates claims of unfair trade practices and suggests appropriate protective measures for domestic industries. The Department of Trade, Industry, and Competition (DTIC) promotes industrial development and competitiveness, including supporting export-focused businesses. The South African Revenue Service (SARS) handles customs procedures, ensuring compliance with tariff regulations and collecting duties. When navigating South Africa's export regulations, consider using fractional executive services for streamlined compliance.
Understanding Export Tariffs and Licensing
South African export regulations cover a range of areas, including export tariffs and licensing requirements. Tariffs are taxes on goods exported from the country, directly affecting exporters' pricing strategies. Licensing ensures exported goods meet specific quality and safety standards. Different product categories have distinct licensing requirements, so it's important to carefully research the regulations pertaining to your specific goods.
The Impact of International Agreements
International trade agreements influence South Africa's export regulations. These agreements affect tariff rates, market access, and other trade-related factors. Exporters must stay informed about these international agreements to optimize their operations and leverage preferential trade deals.
South Africa has seen substantial export growth recently. Exports rose by about $23 billion between 2018 and 2023, totaling $145 billion in 2023. This growth has occurred alongside challenges related to competitiveness and regulatory obstacles. You can find more in-depth statistics at the Observatory of Economic Complexity. A large portion of South Africa's exports are commodities, especially minerals and metals, which can shape the regulatory landscape for businesses.
Adapting to Regulatory Shifts
Regulations are constantly evolving. Legislative changes, new international agreements, and domestic policy shifts create both opportunities and difficulties for exporters. Businesses need to be flexible and monitor regulatory updates. This proactive approach enables companies to adapt strategies, ensuring continued compliance and maximizing their export potential. By understanding the nuances of South African export regulations and working with the relevant regulatory bodies, businesses can successfully navigate the export landscape and achieve sustainable growth in global markets.
Mastering Export Licenses: What Actually Works
Securing the necessary export licenses is crucial for South African businesses engaging in international trade. Simply meeting basic requirements isn't enough. This section explores practical strategies for successful license applications within South Africa's regulatory environment. We'll examine the less obvious aspects of the process, using real-world examples and expert advice.
Understanding the Nuances of Licensing Authorities
Different product categories fall under different regulatory bodies. Agricultural goods require permits from the Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (DAFF), while manufactured products may involve the International Trade Administration Commission (ITAC). Understanding each authority's specific expectations is paramount. This includes not only documented requirements but also the unspoken nuances that can influence your application's outcome.
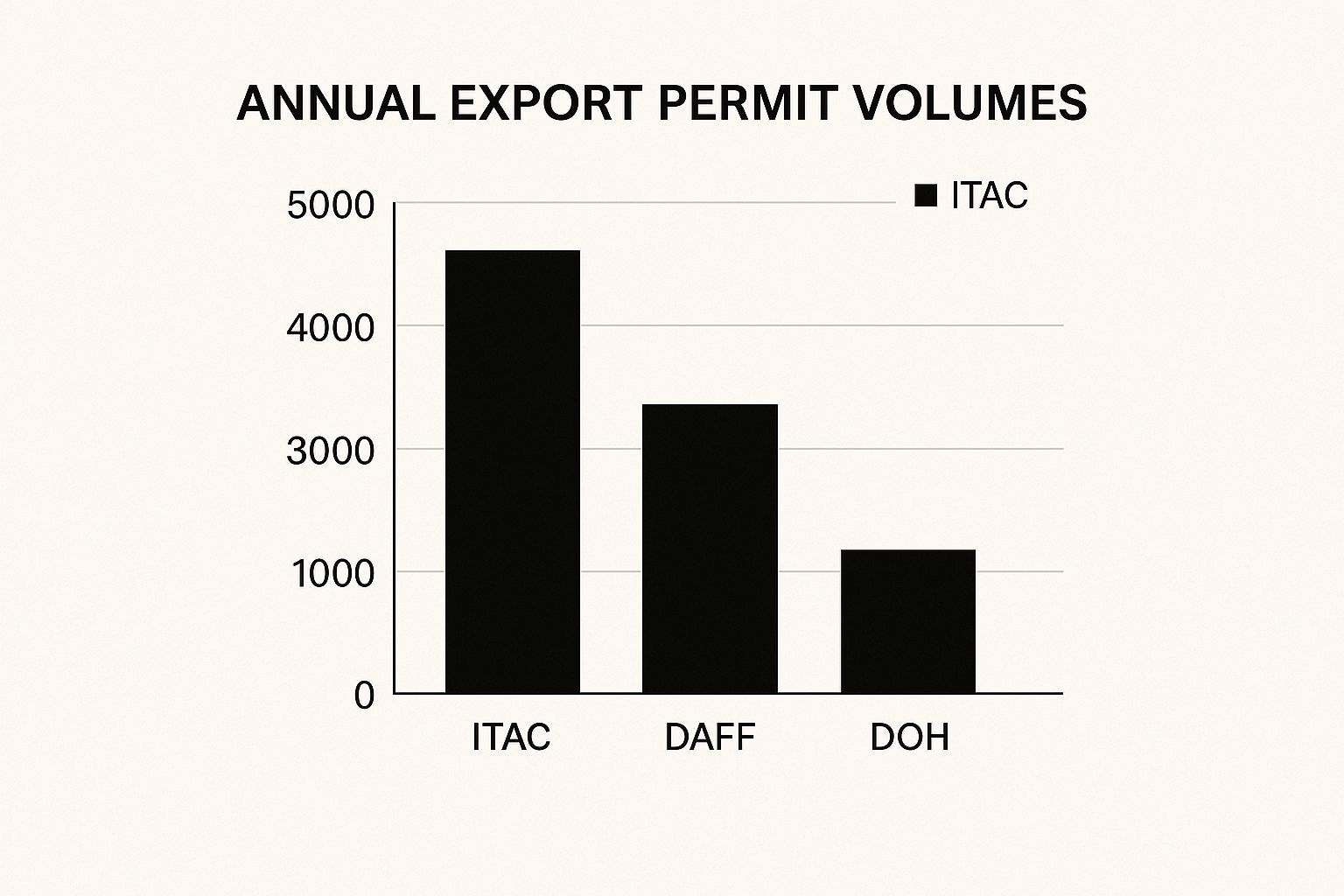
The infographic shows annual export permit volumes processed by three key South African regulatory bodies: ITAC, DAFF, and the Department of Health (DOH). ITAC processes the highest volume (5000), followed by DAFF (3500) and DOH (1200). This data highlights the significant workload and the importance of submitting complete and accurate applications to avoid delays.
To further illustrate the licensing requirements, the following table provides a breakdown by product category:
Export License Requirements by Product Category
A comprehensive overview of the different types of licenses required for various export categories from South Africa.
| Product Category | Licensing Authority | Required Documentation | Processing Time | Special Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural Products (e.g., Fruits, Vegetables) | DAFF | Phytosanitary certificates, commercial invoices, packing lists | 7-10 business days | Adherence to specific import regulations of destination country |
| Manufactured Goods (e.g., Textiles, Automotive Parts) | ITAC | Certificates of origin, commercial invoices, packing lists | 10-14 business days | Compliance with technical regulations and standards |
| Pharmaceuticals | DOH | Product registration certificates, import permits, certificates of analysis | 14-21 business days | Stringent quality control and labeling requirements |
| Precious Metals and Minerals | Department of Mineral Resources and Energy (DMRE) | Export permits, Kimberley Process Certification Scheme (KPCS) certificates | 21-28 business days | Strict control measures to prevent illicit trade |
This table summarizes key documentation and processing times, offering a practical guide for exporters. Remember, specific requirements can vary, so always consult the relevant authority for the most up-to-date information.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Navigating the reasons for application rejections can be challenging. Licensing authorities don't always disclose common pitfalls leading to delays or denials. This lack of transparency can frustrate businesses, especially new exporters. Inconsistencies in documentation, unclear product classifications, or failure to demonstrate compliance with specific regulations are common issues.
South Africa's export control system is linked to its trade policy, balancing domestic industry protection with global market participation. This has increased export-related licensing requirements, impacting sectors like technology. The country's approach to new trade agreements adds another layer of complexity. Learn more about this here. Understanding these potential issues beforehand allows businesses to address them proactively.
Strategies for Faster Approvals
Reducing approval timelines is vital for exporters. Proven strategies can streamline the process, potentially decreasing approval times by up to 40%. These include ensuring meticulous documentation, using online application portals, and proactively communicating with licensing authorities. This proactive engagement demonstrates compliance and can significantly expedite the process. By mastering these strategies, businesses can turn the licensing process from a hurdle into a strategic advantage, facilitating smoother access to international markets and driving growth.
Breaking Through Tariff Barriers: Strategic Approaches

South Africa's tariff system can be complex. However, with the right approach, navigating these regulations can become a source of competitive advantage. This section explores how successful South African exporters use strategic planning to succeed in the global marketplace. It's not just about knowing the rules, it's about knowing how to use them strategically.
Leveraging Trade Agreements for Reduced Tariffs
South Africa participates in several trade agreements that offer preferential tariff rates. These agreements, often established with specific countries or regions, can significantly reduce or even eliminate tariffs on certain goods.
For instance, the Southern African Development Community (SADC) Free Trade Area facilitates duty-free trade among its member states. Similarly, the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) aims to gradually reduce tariffs across the continent. This opens up new and profitable markets for South African exporters. Understanding which agreements apply to your specific products is the first step towards substantial cost savings.
Utilizing Rebate Provisions and Duty Drawbacks
Rebate provisions allow exporters to reclaim duties paid on imported materials that are then used to manufacture exported goods. This prevents South African products from being taxed twice, helping them stay competitive.
Duty drawbacks, on the other hand, offer refunds on duties paid for imported goods that are later re-exported, either in their original state or after processing. Both these provisions can significantly improve your profitability.
Accurate Tariff Classification: Avoiding Costly Mistakes
Correct tariff classification is critical for avoiding penalties and delays. Even small errors in classifying your products can result in significant fines and logistical disruptions. Misclassifying a product under a higher tariff category can have serious consequences.
To avoid these problems, businesses should invest time in understanding the Harmonized System (HS) codes. This standardized system uses names and numbers to classify traded products. Utilizing available tools and resources to ensure accurate classification can minimize risks and streamline export operations.
Building Strong Relationships with SARS Officials
Cultivating positive relationships with South African Revenue Service (SARS) officials can be incredibly beneficial. Open communication and proactive engagement build trust and understanding, which can streamline customs processes. Like any business relationship, building rapport can lead to smoother transactions and quicker resolution of any potential issues. This cooperative approach can be essential for navigating the complexities of South African export regulations.
To help illustrate the variations in tariffs and controls across different sectors, the following table provides a sector-specific breakdown:
The table below, "Comparison of Export Tariffs Across Major South African Export Sectors," analyzes how export tariffs, duties, and controls differ across key South African export industries.
| Industry Sector | Average Tariff Rate | Key Control Measures | Relevant Agreements | Recent Changes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural Products | Varies | Sanitary and phytosanitary (SPS) | SADC, AfCFTA | Increased focus on traceability and sustainability |
| Automotive | Relatively low | Technical regulations | EU-SA EPA | Tariff reductions on certain components |
| Minerals and Metals | Generally low | Export permits | Various | Increased scrutiny on illegal mining and exports |
This table highlights the diverse range of tariffs and control measures across different export sectors. Agricultural products, for example, are subject to varying tariffs and strict sanitary and phytosanitary measures, while the automotive sector benefits from relatively low tariffs and focuses on technical regulations. Understanding these sector-specific nuances is crucial for effective export planning.
Utilizing these strategies, along with staying updated on changes to South African export regulations, is key to successful exporting. Combining these approaches with efficient payment solutions, such as those offered by Zaro, can greatly optimize export operations and fuel growth. By prioritizing proactive compliance and taking a strategic approach to tariffs, South African businesses can effectively compete in the global market.
Navigating Dual-Use Regulations: The Hidden Playbook
South Africa's growing tech sector offers exciting prospects for exporters. However, understanding the export regulations, particularly those related to dual-use goods, can be complex. These regulations apply to items with both civilian and military applications, such as specific software, electronics, and materials. This complexity makes navigating the often "unwritten rules" of this specialized area critical.
Understanding the Challenges of Dual-Use Goods
Dual-use regulations aim to prevent sensitive technologies from reaching the wrong hands while still facilitating legitimate trade. This balance creates unique challenges for South African exporters. For instance, correctly classifying products as dual-use is vital, as misclassification can cause delays, penalties, or legal action. The regulations often involve several government agencies, each with its own procedures.
Practical Frameworks for Product Classification
Accurately classifying your products is a crucial step in navigating dual-use regulations. A strong understanding of the South African National Control List (SANCL), which identifies controlled dual-use items, is essential. This list aligns with international standards but also includes specific South African considerations. Developing a robust internal classification system, perhaps with expert advice, is a worthwhile investment. This ensures accurate and consistent classification, reducing future regulatory risks.
Building Relationships With Regulatory Officials
Formal procedures are essential, but strong relationships with regulatory officials are invaluable. Open communication and transparency can build trust and mutual understanding. This doesn't mean circumventing regulations, but rather proactively engaging with officials to clarify requirements and address concerns. This proactive approach can simplify the export process and build a solid foundation for long-term compliance.

Real-World Successes and Compliance Systems
Examining real-world successful dual-use exports can offer valuable insights. How did these companies handle the regulations? What documentation strategies did they use? Success stories often reveal practical advice and best practices that go beyond standard guidelines. Learning from these examples can help you develop a robust compliance system.
South Africa's export regulations also interact with international frameworks, especially in high-tech and dual-use sectors. The United States, for example, maintains strict export controls for certain technologies to South Africa. In 2022, the U.S. Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) reviewed 352 export license applications for South Africa, totaling $213.2 million. More detailed statistics are available here. This interconnectedness highlights the importance of global regulatory awareness for South African exporters.
Creating a strong compliance system is more than just checking boxes; it’s about building a framework that protects your business. This includes thorough documentation, regular internal audits, and staff training. By proactively addressing these aspects, you turn compliance from a burden into a competitive advantage, demonstrating your commitment to regulatory integrity and building trust with international partners.
Building Export Compliance Systems That Actually Work
Many South African businesses see export compliance as an expensive, time-consuming obligation. However, successful exporters are turning these systems into valuable assets. This section explains how to build compliance frameworks that not only satisfy legal requirements but also strengthen your competitive advantage.
Integrating Compliance into Operational Workflows
Effective compliance isn't a separate entity; it should be seamlessly integrated into daily operations. Think of it as an essential part of the production process, like quality control, rather than a final hurdle. This proactive approach minimizes errors and delays, saving both time and resources in the long term.
For example, embedding compliance checks directly within your CRM system can automate documentation, ensuring accuracy and efficiency from the very beginning of the export process.
Training Strategies for Staff Engagement
Engaged staff are essential for successful export compliance. Training should be an ongoing process that cultivates a culture of compliance, not just a one-time event.
This includes providing regular updates on export regulations in South Africa, developing interactive training modules, and recognizing employees who demonstrate best practices. Gamified training programs, for instance, can make complex subjects like tariff classification more engaging and effective.
Technology Solutions for Different Business Sizes
Technology can greatly simplify compliance, but the ideal solution depends on the scale of your operations. Smaller businesses might benefit from cloud-based document management systems. Larger enterprises, on the other hand, might need specialized compliance software that integrates with their existing ERP systems.
Consider platforms like Zaro, which automates compliance and provides transparent foreign exchange (FX) solutions. This streamlines export operations for businesses of all sizes.
Maintaining Compliance Visibility Across Supply Chains
Today's supply chains are incredibly complex, making maintaining compliance visibility a significant challenge. Leading exporters leverage technology and collaboration to keep track of every step.
This could involve implementing blockchain technology for tracking goods or conducting regular audits of international partners. It's like having a GPS tracker for your products, ensuring compliance at every stage of the journey.
Implementing Effective Audit Protocols
Regular audits are vital for pinpointing compliance gaps and identifying areas for improvement. These audits should be thorough, covering everything from documentation to training procedures.
The goal isn't to assign blame, but to promote continuous improvement. Conducting mock audits, for example, can prepare your team for real inspections and uncover potential vulnerabilities.
Building Resilient and Adaptable Systems
Export regulations in South Africa are constantly changing. Your compliance system must be flexible enough to adapt. This involves establishing processes for monitoring regulatory changes, implementing updates effectively, and fostering a culture of continuous learning.
This proactive approach ensures that your export business can navigate regulatory changes smoothly without disrupting operations. A resilient compliance framework is not an expense; it's a strategic investment in your future success.
The Future of South African Export Regulations: Be Prepared
Keeping up with South Africa's evolving export regulations is no longer optional, but essential for success. This involves understanding emerging trends and adapting your export strategy proactively. This section offers valuable insights from policy experts and trade professionals, preparing you for what lies ahead in South African export regulations.
The AfCFTA's Impact on Regional Trade
The African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) is significantly changing regional trade, creating both opportunities and challenges for South African exporters. The agreement's gradual reduction of tariffs across the continent opens doors to new markets.
However, it also brings increased competition. Businesses must understand the AfCFTA's specific rules and their potential impact on target markets. Harmonizing regulations across the continent may simplify some export procedures while introducing new compliance requirements.
Sector-Specific Regulations
Expect varying levels of regulatory scrutiny across different sectors in the coming years. Industries with environmental impacts, for instance, may face stricter sustainability requirements. Increased globalization and technological advancements could also lead to tighter regulations on specific goods. For more information on compliance systems, explore insights into Financial Compliance. Conversely, some sectors might see a reduced regulatory burden as the government promotes specific industries. Staying informed about these sector-specific changes is crucial.
Digital Transformation of Export Procedures
Digital transformation is set to reshape South African export procedures. This includes online platforms for license applications, electronic documentation, and automated customs processes. While these changes aim to streamline operations, businesses will need to adapt their internal systems. Investing in the right technology and training staff on these new systems will be essential for maintaining efficiency.
Sustainability in International Trade
Sustainability is taking center stage in international trade. Forward-thinking businesses are already preparing for more stringent sustainability-focused regulations. This includes adopting environmentally friendly practices, sourcing sustainable materials, and implementing transparent supply chain tracking. Consumers and international partners are increasingly demanding these standards, making sustainability a competitive necessity.
Controlled Goods Classifications
The classification of controlled goods, especially dual-use items, is constantly changing. Businesses handling these goods must monitor regulatory updates and align their internal classification systems with the latest South African National Control List (SANCL). Failing to do so can result in significant penalties and reputational damage.
Verification Requirements for Increased Transparency
Expect increased verification requirements for exports in South Africa. This includes stricter due diligence processes for exporters, enhanced record-keeping, and more frequent audits. These measures aim to improve transparency and prevent illegal trade. Implementing robust compliance systems adaptable to these changes is crucial for staying ahead of the curve.
Successfully navigating these evolving regulations requires a proactive and adaptable approach. By understanding the trends and establishing appropriate compliance systems, South African businesses can not only survive but thrive in the global marketplace. Zaro, a fintech platform for cross-border payments, can help South African businesses manage these complexities. Zaro offers transparent FX solutions, automating compliance and simplifying international transfers. Learn more at https://www.usezaro.com.
