The Real Cost of Trading: Why Forex Broker Fees Matter
Imagine nailing a perfect forex trade, predicting the Rand's fluctuation against the dollar with pinpoint accuracy. Yet, when you check your profits, they’re disappointingly low. Where did the extra money go? This frustrating scenario is all too common for traders who haven't fully grasped the impact of forex broker fees.
These seemingly insignificant costs can significantly erode your earnings over time. Understanding these fees provides invaluable insight into your trading account, revealing hidden expenses that can ultimately determine your success or failure.
This isn't about becoming a market guru; it's about sound financial management. Seasoned South African traders know that consistent profitability often hinges on understanding and minimizing these costs. Think of trading like running a business: overlooking overheads is a recipe for disaster.
Forex trading operates on the same principle. Ignoring broker fees is akin to ignoring rent – it will eventually catch up with you.
Decoding the Fee Landscape
Forex broker fees aren’t always transparent. Brokers utilize diverse fee structures, some more straightforward than others. One key fee is the spread, the difference between the buying (ask) and selling (bid) price of a currency pair. Think of it as the markup a car dealership adds to a vehicle's price.
Then there are commissions, explicit charges per trade. This is similar to paying a brokerage fee when buying or selling shares on the Johannesburg Stock Exchange (JSE).
There are also overnight fees, also called swap rates, for holding positions overnight. Imagine borrowing Rand to buy US dollars. You're effectively paying interest on the borrowed Rand while receiving interest on the dollars you hold. The difference between these interest rates constitutes your overnight fee, which can work for or against you depending on prevailing interest rates.
In South Africa, forex trading fees vary considerably among brokers. Some brokers offer spreads from as low as 1 pip for major currency pairs, while others might impose higher spreads or commissions, typically between $5 and $10 per lot traded. For a deeper dive into the specifics of forex broker fees in South Africa, check out this helpful resource: Discover more insights about forex broker fees in South Africa.
Finally, there are deposit and withdrawal fees, the costs associated with transferring funds in and out of your trading account. These can be a small percentage or a fixed amount, depending on the transfer method and the broker. This is much like the fees you might pay for interbank transfers.
The Psychology of Fees
Some brokers employ psychological tactics with their fee structures. A deceptively low spread might mask other hidden charges. This is why understanding the total cost of trading is so vital. Don’t just focus on individual fees; consider their cumulative effect.
Recognizing these tactics empowers you to make informed choices. By understanding forex broker fees, you can select a broker that aligns with your trading style and helps you maximize your profits. It’s about seeing beyond the marketing hype and understanding the true cost of trading in the forex market.
Spreads Decoded: The Art of Paying Less Per Trade
Think of the spread in forex trading like the commission a real estate agent charges – it's the broker's cut for facilitating your trade. This seemingly small fee can significantly impact your overall profits, especially for active traders in South Africa. Spreads come in two main flavors: fixed spreads and variable spreads. Fixed spreads offer predictable costs, like a flat delivery fee. Variable spreads, on the other hand, fluctuate with market conditions, similar to surge pricing on a ride-sharing app during peak hours.
Understanding Spreads in South African Trading
Let's paint a picture. Imagine you're trading USD/ZAR. A broker with a 1-pip spread compared to another with a 2-pip spread might not seem like a big deal. But consider this: if you make 10 trades a day with a standard lot (100,000 units) over a year, that 1-pip difference can translate to a considerable amount in Rands. Choosing a broker with competitive spreads is crucial, particularly for frequent traders in South Africa.
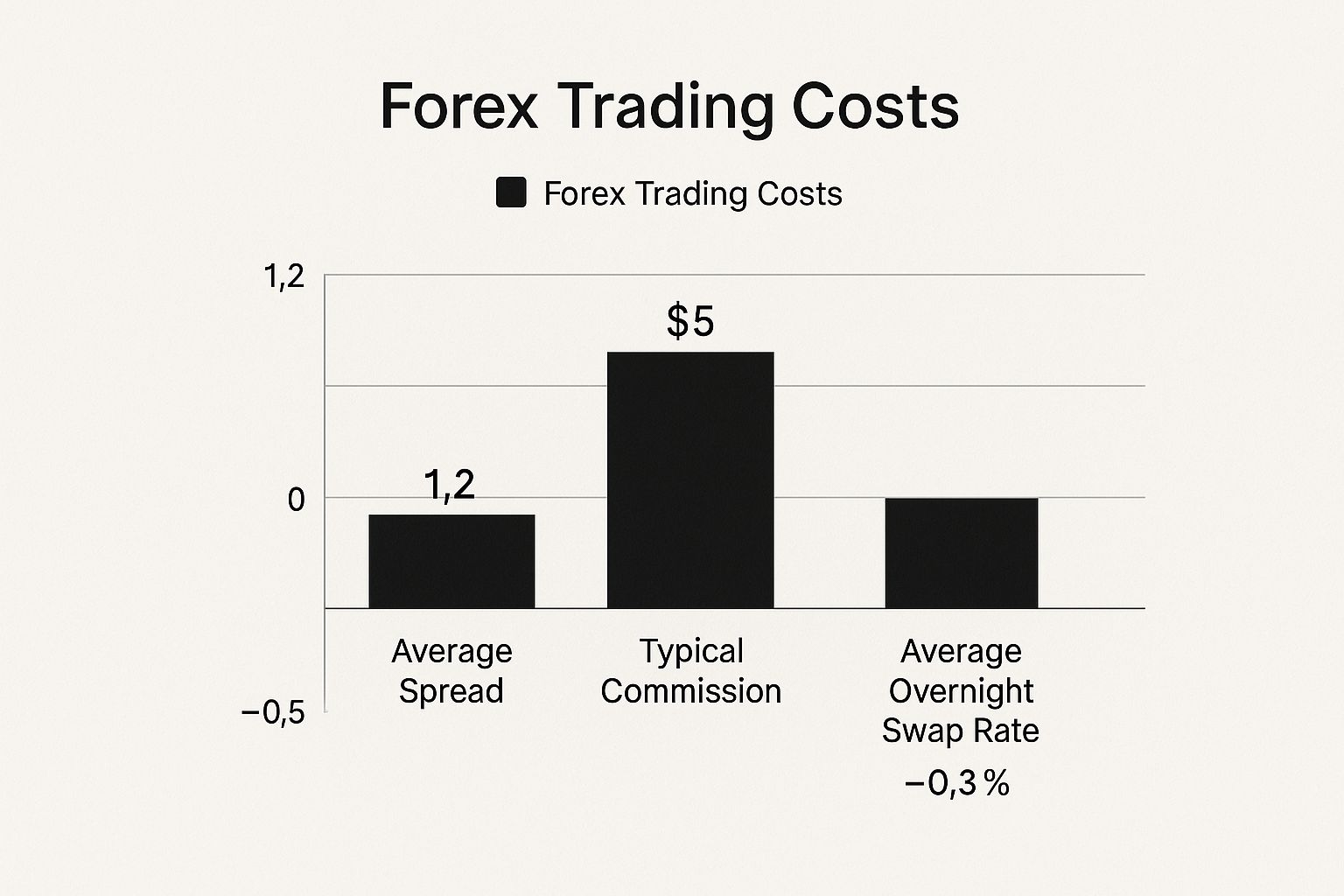
The infographic above illustrates typical forex broker fees, showing the average spread (1.2 pips), commission ($5 per standard lot), and overnight swap rate (-0.3%). It visually reinforces how these seemingly small costs accumulate, impacting your bottom line. These aren't just numbers on a screen; they represent real money gained or lost.
Navigating Variable Spreads: Market Volatility and Liquidity
Variable spreads aren't always the villain. During calm market conditions, they can even be lower than fixed spreads. However, when volatility kicks in – think major news events or market openings – variable spreads can widen drastically. This is especially pertinent for South African traders, as the Rand is often sensitive to global market swings.
Think of it like buying concert tickets on the resale market. When demand surges, prices skyrocket. Similarly, during volatile forex market conditions, decreased liquidity causes spreads to widen, making it more expensive to enter or exit trades.
Evaluating Spread Competitiveness: Beyond the Headlines
Don't be swayed by flashy advertised spreads alone. Savvy traders understand that true competitiveness depends on how spreads behave under pressure. A broker boasting ultra-low spreads might not seem so attractive when those spreads balloon during periods of volatility or thin liquidity.
Timing Is Everything: Minimizing Spread Impact
Strategic trade timing can significantly reduce your spread costs. Avoid trading during periods of high volatility unless your strategy specifically calls for it. For instance, trading during major news releases can expose you to wider spreads, potentially eroding your profits.
South African traders can mitigate this risk by steering clear of volatile periods, particularly around global news events that impact the Rand. Understanding market opening and closing times, especially the overlap between the London and New York sessions (when liquidity and spreads are often more favorable), is also crucial.
Let's look at a quick comparison of spreads:
Major Currency Pair Spread Comparison
A comparison of typical spreads offered by different broker types for popular forex pairs traded by South African investors
| Currency Pair | ECN Brokers | Market Makers | Impact on R1000 Trade |
|---|---|---|---|
| USD/ZAR | 0.5 pips | 1.5 pips | R7.50 vs R22.50 |
| EUR/ZAR | 0.8 pips | 2.0 pips | R10 vs R25 |
| GBP/ZAR | 1.0 pips | 2.5 pips | R12.50 vs R31.25 |
As you can see from the table, the impact on even a R1000 trade can be noticeable between broker types. ECN brokers, generally offering tighter spreads due to direct market access, result in lower costs per trade.
By combining smart timing with a broker offering competitive and transparent spreads, you'll take a significant step towards more profitable trading.
Commission Structures: When Transparency Wins

Imagine walking into two restaurants. The first hands you a detailed menu, each dish individually priced. The second offers an all-you-can-eat buffet for a fixed price. Commission-based forex brokers are like the first restaurant – upfront about their execution fees. Spread-only brokers, like the buffet, bundle the cost into the spread. This can make it tricky to compare brokers and understand the true cost of your trades.
This transparency is especially helpful for South African traders who know how to break down forex broker fees. A commission-based broker might charge a small fee, say $5 per lot, but offer a raw, interbank spread. This raw spread is generally much tighter than the marked-up spreads you see with spread-only brokers.
Unmasking Hidden Costs: Commission vs. Spread
Let's look at a practical example. Imagine trading USD/ZAR. A spread-only broker offers a 2-pip spread. A commission-based broker offers a 0.5-pip spread and a $5 commission per lot. For larger trades, the commission-based broker actually becomes cheaper.
Let's say you make a 1-lot trade (100,000 units). With the spread-only broker, you pay R200 (assuming a ZAR/USD rate of R20). The commission-based broker charges R50 for the spread and R100 commission (assuming $5 equals R100), totaling R150. Already, the commission-based broker is less expensive.
This difference becomes even clearer with larger trades. A 5-lot trade with the spread-only broker costs R1000. The commission-based broker's spread cost is R250, plus the fixed R100 commission, totaling R350 – a substantial saving. This highlights the potential benefits of commission-based accounts, especially for active South African traders.
Professional-Grade Execution: The Commission Advantage
Many professional traders gravitate toward commission-based accounts for their professional-grade execution. These accounts often provide Direct Market Access (DMA), letting traders interact directly with the interbank market. This usually translates to faster execution and tighter spreads, which can be vital in volatile markets.
Choosing the Right Structure: A Personalized Approach
No single fee structure suits everyone. The best choice depends on how often you trade, your position sizes, and your profit goals. High-frequency traders might prefer commission-based accounts with their tight spreads, while occasional traders might find spread-only accounts easier to manage. Analyze your trading habits and calculate your potential costs under different fee structures. Understanding forex broker fees helps you make smart choices, optimize your trading costs, and boost your profitability in the South African market.
Overnight Fees Demystified: The Cost of Holding Positions
Holding a forex position overnight isn't simply waiting for the market to shift in your favor. It's more like borrowing one currency to buy another. Think of it as borrowing Rand from a friend to purchase US dollars. You'd probably agree to pay your friend a small amount for the loan. In the same way, your broker facilitates this international "loan" when you hold a forex position overnight, charging a fee called a swap rate. This is a crucial aspect of forex broker fees, and understanding how it works can significantly impact your profits.
The Mechanics of Swap Rates: Interest Rate Differentials
Swap rates are based on the interest rate differential between the two currencies in the pair you're trading. If the interest rate of the currency you're buying is higher than the one you're selling, you'll typically receive a positive swap. On the other hand, if the interest rate of the currency you're selling is higher, you'll pay a negative swap. It's similar to the difference between earning interest on your savings account and paying interest on a loan.
For example, imagine you're long USD/ZAR (buying USD and selling ZAR), and the US interest rate is higher than the South African interest rate. In this scenario, you'll likely earn a positive swap, a small reward for holding the position overnight.
Central Banks and Seasonal Patterns
Central banks wield considerable influence over interest rates, and consequently, swap rates. Changes in monetary policy by the South African Reserve Bank (SARB), for example, can directly affect the cost of holding certain overnight positions involving the Rand. This influence extends to other central banks globally, creating a complex web of factors that affect swap rates.
Seasonal patterns can also play a role. Certain times of the year, due to economic cycles or specific market conditions, might see consistently higher or lower swap rates for certain currency pairs.
Managing Swap Rates: Strategies for Success
Savvy traders don't just passively accept swap rates; they actively manage them. One common approach is closing positions before the swap is applied, usually around 5 pm New York time. Another strategy is focusing on carry trades, where you profit from the positive interest rate differential between two currencies. It's like earning interest simply by holding a position – that’s the potential of a well-executed carry trade.
South African Market Insights
The impact of overnight fees is particularly important in the South African forex market. Because of the relatively high interest rate environment in South Africa compared to some other developed countries, specific currency pairs involving the ZAR can present attractive swap opportunities. For instance, traders sometimes explore carry trades involving the ZAR against currencies with lower interest rates. However, it's vital to remember that interest rate differentials, and thus swap rates, are always changing.
By understanding the mechanics of overnight fees and using strategic management techniques, South African traders can minimize costs and perhaps even profit from the nuances of swap rates, turning a potential expense into a strategic advantage.
Funding Costs: The Expensive Journey In and Out
Moving your hard-earned trading profits shouldn't feel like an obstacle course. But for many South African traders, accessing those earnings can reveal some surprising costs. Funding costs in forex trading go beyond simple transaction fees. Things like currency conversion charges, processing delays, and intermediary costs can quietly chip away at your returns. It’s a bit like budgeting for a road trip – you plan for petrol, but then tolls, detours, and snacks start adding up.
Understanding the Funding Landscape in South Africa
Let's explore the different ways South African traders can fund their accounts and withdraw their profits. Think of traditional bank wires as sending a package through the post office – it might be secure, but it can be slow and expensive. On the other hand, modern e-wallet solutions are like using a courier service – faster, but potentially with transaction limits or currency conversion fees. Each method has its own set of pros and cons.
Currency Conversion: The Hidden Cost
One expense that often flies under the radar is currency conversion fees. Imagine exchanging Rands for dollars at a currency exchange booth – they have different buying and selling rates, pocketing the difference as profit. Similarly, when you fund your trading account or withdraw profits, your broker or payment provider might add a markup to the exchange rate. Even a small percentage can have a big impact, especially on larger amounts. For example, a 2% conversion fee on a R10,000 withdrawal means you lose R200.
Processing Times and Capital Availability
Processing times also play a role in how much trading capital you have available. A delayed withdrawal means your money is tied up, potentially causing you to miss out on profitable trades. Imagine needing to jump on a great market opportunity, but your funds are stuck in transit due to slow processing. Knowing the processing times for different funding methods is key to staying agile in the market.
Minimizing Funding Costs: Strategies for South African Traders
The good news is, there are ways to reduce these costs. For example, you might be able to negotiate lower fees with your broker, especially if you have a larger account balance. Using a local bank account in the same currency as your trading account can eliminate or minimize currency conversion charges. And exploring alternative withdrawal methods like debit cards or e-wallets might reveal more cost-effective options.
Navigating International Transactions
Many South African traders work with international brokers, which adds another layer of complexity. It’s important to understand local regulatory requirements and international transfer procedures. Think of it like understanding customs regulations when shipping goods internationally. This knowledge helps you avoid unnecessary delays and stay on the right side of the rules.
By understanding the ins and outs of funding costs and using smart strategies, South African traders can protect their profits and maximize their returns. It's all about making informed decisions, choosing the right funding methods, and navigating the international financial landscape effectively.
Your True Trading Costs: The Complete Picture

Many traders compare forex broker fees to grocery shopping, focusing on individual items instead of the total basket cost. But this can be a trap. True trading costs go beyond the advertised spreads and commissions. They include your personal trading style, how much you trade, how long you hold positions, even how you fund your account. It's like buying a car: the sticker price is just the start. There's also fuel, insurance, and maintenance.
Calculating Your Actual Trading Expenses
To truly grasp your forex broker fees, you need a holistic approach. This means looking beyond the obvious and understanding how different fee structures interact with your individual trading habits.
For example, a day trader making many small trades will feel the pinch of spreads more than a swing trader holding positions for several days or weeks, who needs to watch out for overnight fees.
Your choice of currency pairs and typical trade sizes also play a big role. Trading exotic pairs often comes with wider spreads than major pairs like USD/ZAR. Larger trades magnify the impact of both spreads and commissions.
The Power of Historical Data Analysis
Here's where looking at your past trades becomes incredibly useful. By applying different broker fee models to your historical data, you can turn abstract fee comparisons into real Rand-and-cent figures. This reveals precisely how different forex broker fees would have affected your actual profits and losses.
Imagine replaying your trades under different fee scenarios and seeing the impact on your bottom line – that’s the power of historical data analysis. It’s especially vital for traders in South Africa who want to understand forex market dynamics and choose the right broker. Discover more insights about using historical forex data.
Building a Personalized Cost Comparison Framework
Using clear examples and practical tools, you can create a personalized cost comparison framework tailored to you. This framework considers your preferred currency pairs, typical position sizes, and how often you trade.
Think of it as a custom budget for your forex trading, empowering you to make informed decisions based on hard data, not just marketing. This is particularly important for South African traders navigating the forex market.
Let's illustrate this with a practical example. The table below shows how different fee components can add up depending on your trading activity.
Total Trading Cost Calculator Example A breakdown showing how different fee components combine to create the total cost for various trading scenarios
| Trading Scenario | Spread Cost | Commission | Overnight Fees | Total Monthly Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 trades/month, 0.5 lot, major pair | R500 | R250 | R100 | R850 |
| 100 trades/month, 0.1 lot, exotic pair | R400 | R100 | R50 | R550 |
| 20 trades/month, 1 lot, major pair | R400 | R200 | R200 | R800 |
As you can see, even seemingly small differences in fees can significantly impact your overall costs. By understanding these nuances, you can make informed choices about which broker best suits your needs. It's about choosing a broker whose fee structure works with your trading strategy, not against it. This personalized approach puts you in control and helps you maximize your potential profitability.
Smart Cost Management: Your Optimization Roadmap
Successfully navigating the forex market isn’t just about predicting which way a currency will jump. It’s also about understanding the costs tied to every trade you make. The goal isn’t to find the absolute cheapest broker. Think of it like crafting a recipe: you need the right balance of ingredients—low costs, reliable execution, and trustworthy service—to create a delicious outcome. This is particularly important for South African traders engaging with the global market.
Beyond Basic Comparisons: Strategies for Success
Savvy South African traders employ cost management strategies that go beyond simply comparing advertised fees. They know the value of negotiation, particularly as their trading activity grows. They also understand how smart timing can reduce costs and use portfolio management techniques to minimize those pesky overnight charges.
Negotiating Better Terms: Leverage Your Volume
As your trading volume increases, so does your power to negotiate. It's like buying in bulk at the supermarket: the more you buy, the better the price you can often get. Different brokers react to different negotiation strategies. For instance, with an ECN broker, you might focus on lowering the commissions per lot. With a market maker, negotiating tighter spreads or lower initial deposit requirements could be more effective.
Timing the Market: Minimizing Cost Impact
When you enter and exit a trade can significantly impact your costs. Try to avoid trading during volatile periods, such as major news announcements or market openings, when spreads tend to widen. Imagine trying to grab a taxi during rush hour – the fares are usually inflated. Similarly, a volatile forex market can lead to higher transaction costs. Strategic timing helps you avoid these premium prices.
Portfolio Optimization: Reducing Overnight Charges
Holding positions overnight incurs swap fees, which can chip away at your profits. Optimizing your portfolio can help minimize these. For instance, consider reducing your exposure to currency pairs with high negative swap rates, or exploring opportunities to profit from positive carry trades. Think of it like managing your credit card debt – you want to minimize those high interest payments.
The Hidden Costs of Cheap Brokers: A Reality Check
Those ultra-low fees can be tempting, but watch out for hidden costs. Some brokers might offer incredibly low spreads but compensate with higher commissions or unreliable order execution. It’s like buying a cheap phone that constantly glitches – those initial savings are quickly offset by frustration and ultimately, the need to buy a new one. Focusing solely on price when choosing a broker can end up being more expensive in the long run. Look for a balance between cost and quality of service. Sometimes, paying a slightly higher fee for better execution or reliable customer service can greatly boost your overall profitability.
Building Long-Term Profitability: A Practical Framework
Managing trading costs effectively is a continuous process, not a one-time fix. Create a practical framework that combines cost awareness, strategic planning, and ongoing optimization. Regularly review your trading costs, explore new strategies for reducing fees, and always look at the total cost of trading, not just the individual components. A proactive approach to cost management sets you up for long-term success in the competitive South African forex market.
Ready to take control of your cross-border payments and eliminate hidden fees? Discover how Zaro can empower your South African business to thrive in the global marketplace. Visit Zaro today and experience the future of international finance.
