Understanding FSP Number Meaning in South African Finance

In the South African financial sector, the FSP number carries significant weight. It's essential for both financial service providers and their clients. But what exactly does this number represent, and why is it so important? This section explains the meaning of FSP numbers and their vital role in South Africa's financial system.
An FSP number is a unique identifier given to Financial Services Providers (FSPs) by the Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA). This number serves as proof that a provider is authorized to offer financial services in South Africa. Think of it as a badge of legitimacy, assuring clients that the provider operates under regulatory supervision. This framework promotes trust and transparency within the financial industry.
The FSP number confirms that a provider adheres to the regulations established by the FSCA. This includes meeting specific capital and liquidity requirements, which are designed to maintain financial stability. Obtaining an FSP number demonstrates that the provider has met these stringent requirements. For more detailed information on FSP registration, visit: Learn more about FSP registration. This oversight is crucial for protecting consumers and preserving the integrity of the financial system.
Decoding the Importance of the FSP Number
For South African businesses, especially those engaged in international trade, understanding the FSP number is vital. It ensures they are working with legitimate financial institutions. This is particularly important for companies using platforms like Zaro for cross-border payments. Verifying the FSP number of their payment provider helps businesses mitigate the risk of fraud and ensure secure transactions.
The FSP number is also critical for consumer protection. It provides a way to verify the credentials of financial service providers, offering peace of mind to individuals and businesses. It also allows for greater transparency and accountability within the financial sector. This creates a more secure and trustworthy environment for everyone.
To further illustrate how the FSP number fits within the South African regulatory landscape, the following table compares it to other common financial registrations. It highlights key differences in their purpose, regulatory body, and renewal period.
FSP Number vs Other Financial Registrations
| Registration Type | Regulatory Body | Purpose | Renewal Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| FSP Number | Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA) | Authorizes the provision of financial services | Annually |
| Financial Advisory and Intermediary Services Act (FAIS) License | Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA) | Regulates financial advisors and intermediaries providing advice and intermediary services | Annually |
| Registration of Accountants and Auditors (RAA) | South African Institute of Chartered Accountants (SAICA) | Registers professional accountants and auditors in South Africa | Annually |
| Tax Practitioner Registration | South African Revenue Service (SARS) | Authorizes individuals to practice as tax professionals | Annually |
This table clarifies the distinct role of the FSP number compared to other financial registrations. While all contribute to regulating the financial sector, the FSP number specifically authorizes the provision of financial services, falling under the jurisdiction of the FSCA. Its annual renewal ensures ongoing compliance and accountability.
The FSP Number and Regulatory Compliance
The FSP number isn't just a number; it signifies adherence to a strict regulatory framework. This compliance ensures providers maintain appropriate standards of conduct and financial stability, reinforcing trust and providing a layer of protection for consumers. This system benefits both individual clients and the overall financial landscape.
How FSP Numbers Empower Consumers
The FSP number is a powerful tool for consumers to verify the legitimacy of financial service providers. By checking a provider's FSP number on the FSCA website, consumers can confirm registration status and regulatory compliance. This empowers them to make informed choices and avoid potential scams. This accessible verification process is crucial for consumer protection.
Understanding the FSP number equips consumers and businesses with the knowledge to navigate the financial world with confidence. By recognizing the importance of this identifier, informed decisions can be made, and financial interests can be protected. The FSP number is a cornerstone of trust and transparency in the South African financial industry.
The FAIS Act Foundation: Legal Requirements Behind FSP Numbers

An FSP number signifies a commitment to professional standards and regulatory compliance within South Africa's financial services sector. This commitment originates from the Financial Advisory and Intermediary Services (FAIS) Act of 2002, the cornerstone of FSP regulation. This Act establishes the framework governing how FSPs operate and ensures they adhere to stringent requirements. It provides the basis for issuing and regulating FSP numbers, aiming to regulate financial services providers and ensure professionalism and trustworthiness. For a deeper look into the FAIS Act, you can explore this topic further.
Key Provisions of the FAIS Act
The FAIS Act includes various provisions designed to protect consumers and maintain the integrity of the financial services industry. These regulations make the FSP number a powerful symbol of trust.
The Act dictates minimum competency requirements for financial advisors, ensuring they have the necessary knowledge and skills. It also mandates ongoing compliance obligations, meaning FSPs must continuously adhere to regulations after registration. This reinforces accountability and maintains high industry standards.
Categorizing Financial Service Providers
The FAIS Act defines different categories of financial service providers, each with specific regulations and requirements. This categorization ensures appropriate regulation for each type of provider and helps consumers understand each FSP's area of expertise. This clarity is vital for connecting clients with the right financial professionals.
Fit and Proper Requirements
The FAIS Act introduces "fit and proper" criteria for FSP applicants. This means applicants must demonstrate competence, ethical conduct, and financial soundness. This criterion ensures that only those meeting high standards of integrity and professionalism can operate in the financial services sector, adding another layer of security for consumers.
Continuous Monitoring and Enforcement
The FAIS Act establishes continuous monitoring systems to ensure registered providers maintain their standards. The Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA) actively oversees FSPs, conducting regular reviews and investigations. This ongoing monitoring ensures adherence to the FAIS Act and protects consumers from unethical or incompetent practices, reinforcing the FSP number as a symbol of ongoing compliance. This oversight demonstrates the FSCA’s commitment to upholding high industry standards, further strengthening the meaning of the FSP number.
Getting Your FSP Number: The Complete Registration Journey
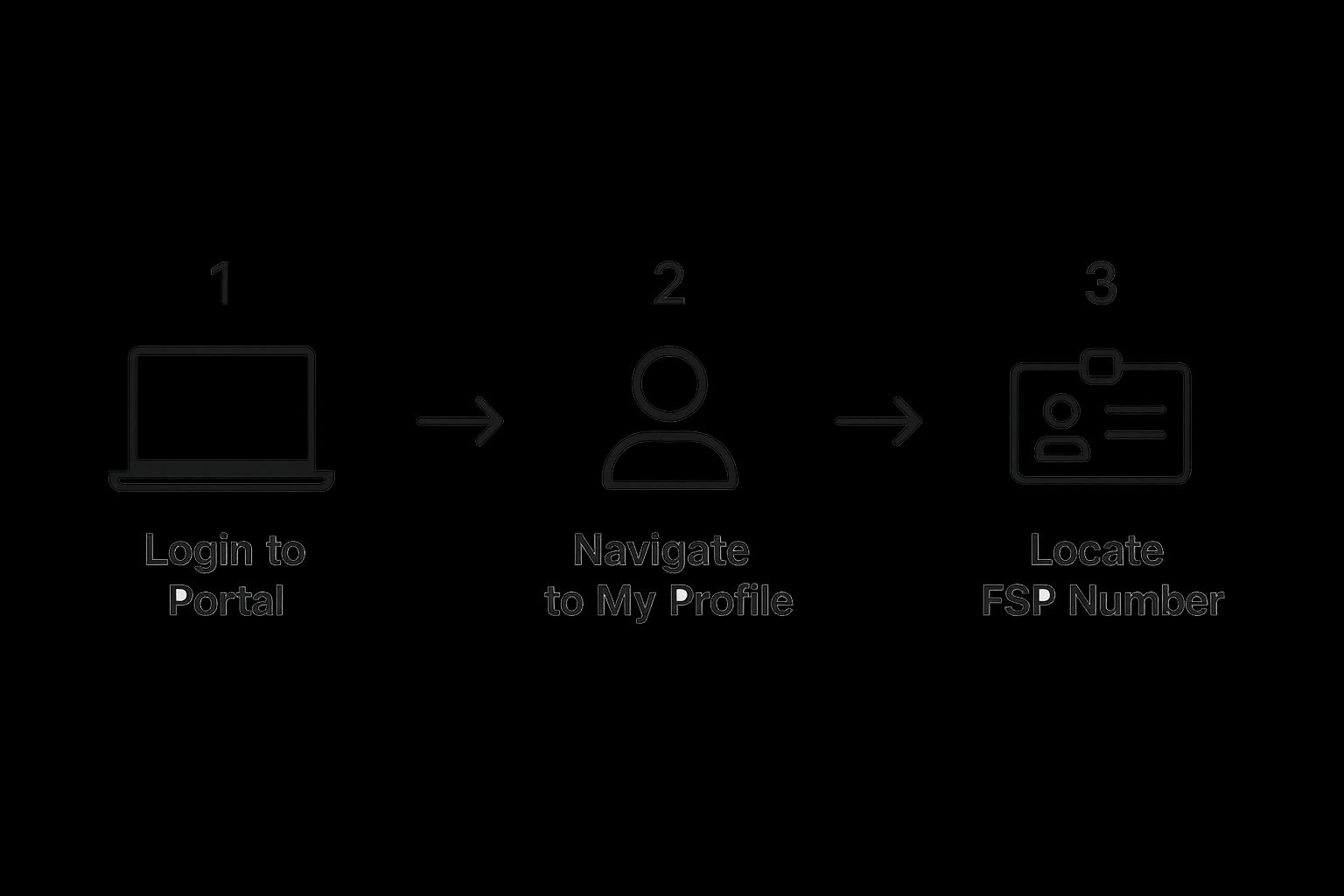
This infographic visualizes the process of finding your FSP number after logging into the FSCA portal. It simplifies the steps into three key actions: logging in, navigating to your profile, and locating your FSP number. This visualization highlights how easy it is to access your number once registration is complete. Now, let's explore the journey of obtaining that number.
Preparing For Your FSP Application
The process of acquiring your FSP number begins with thorough preparation. This involves gathering the necessary documents, understanding the qualifications, and ensuring your business meets the capital adequacy requirements. This groundwork is essential for a smooth registration process.
Documentation: Compile all required documents. This includes business registration certificates, compliance manuals, and financial statements. Organized documentation demonstrates your preparedness to operate as a registered FSP.
Qualifications: Ensure you and your key personnel meet the required qualifications and experience. This shows professional competence and builds trust with clients.
Capital Adequacy: Demonstrate financial stability by maintaining sufficient capital to cover potential risks. This assures the FSCA of your business's long-term viability and ability to protect client funds.
Navigating The FSCA Application Process
After compiling the necessary documents, the next step is formally applying through the FSCA’s online portal. This involves completing the application, providing supporting documents, and awaiting review. This typically takes around three months if all requirements are met upfront. Once registered, FSPs must renew their license annually. Learn more about FSPs. Knowing this timeline allows for proper planning.
Post-Approval: Maintaining Your FSP Status
Obtaining your FSP number is a significant milestone, but the journey continues. You must understand the ongoing compliance requirements to maintain your status. These include annual license renewals and adhering to the FSCA’s monitoring procedures. This ensures your business continues to operate legally and maintains client trust.
Common Mistakes And Best Practices
Many applicants make common mistakes that can delay approval. These include submitting incomplete documentation, failing to meet capital adequacy requirements, or overlooking key personnel qualifications. By understanding the FSCA’s expectations, you can proactively address these areas and improve your chances of timely registration.
By following these steps, you can confidently navigate the FSP registration process, secure your FSP number, and establish your presence as a trusted financial services provider in South Africa. This builds credibility and assures clients of your commitment to regulatory compliance.
SA's FSP Landscape: Industry Scale and Market Reality
South Africa's financial services sector is known for its strength and diversity, a key sign of a developed economy. Understanding the size and scope of this sector is vital for both businesses and consumers. This involves not only knowing what an FSP number is but also understanding the significant number of FSPs operating within the country. This knowledge provides valuable context for the market and its impact.
In 2018, there were approximately 11,300 registered FSPs, with around 165,000 representatives working across these entities. This demonstrates the substantial reach of financial advisory and intermediary services in South Africa. More detailed statistics can be found here. These figures emphasize the significant role these services play in the national economy.
The following table, "FSP Industry Statistics Overview," presents key statistics showcasing the scale and distribution of Financial Services Providers across South Africa. It provides a snapshot of the industry in 2018, offering insights into its composition and reach.
| Metric | Number | Percentage of Total | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Registered FSPs | 11,300 | - | 2018 |
| FSP Representatives | 165,000 | - | 2018 |
The table above highlights the substantial presence of FSPs and their representatives in the South African financial landscape. This underscores the industry's significant contribution to employment and economic activity.
Diversity Within the FSP Ecosystem
The South African FSP landscape is incredibly diverse. It includes a wide range of providers, from small, specialized firms focusing on niche products to large, multinational institutions offering a full spectrum of services.
This diversity creates a competitive market, giving South African consumers a wide variety of choices. It also allows for specialization, which benefits both businesses and individuals seeking targeted financial expertise.
Geographic Distribution and Market Concentration
FSPs are not evenly distributed across South Africa. Some areas have a higher concentration of providers than others. This uneven distribution presents both challenges and opportunities.
It reveals potential gaps in access to financial services, especially in underserved areas. It also indicates potential market saturation in more densely populated areas, making it harder for new FSPs to establish themselves.
Employment and Economic Impact
The large number of representatives employed in the FSP sector shows its substantial contribution to the South African economy. This includes direct employment within FSPs and indirect contributions to related industries.
This job creation stimulates economic growth and reinforces the importance of a well-regulated financial sector. This, in turn, strengthens the overall financial health of the country.
Emerging Trends and Market Dynamics
The financial services sector is constantly changing, with new trends and innovations continually appearing. These trends shape how FSPs operate, the services they offer, and how they engage with their clients.
Staying up-to-date on these changes is important for both FSPs and consumers. For providers, it's a matter of adapting and thriving in a dynamic market. For consumers, it allows for making well-informed financial decisions. Understanding these market dynamics is crucial for navigating the evolving financial landscape.
Consumer Protection Through FSP Registration Standards
Your FSP number signifies more than just regulatory compliance. It represents a robust system designed to protect consumers' financial interests. This system works tirelessly to ensure that your interactions with financial service providers are fair, transparent, and secure.
How FSP Registration Protects Consumers
The FSP registration process creates a comprehensive protection framework. This framework includes measures like mandatory professional indemnity insurance, covering client losses due to provider negligence or misconduct.
Strict conduct of business rules also dictate how providers interact with clients, promoting ethical behavior and preventing exploitation. This establishes a baseline level of protection for all consumers interacting with registered FSPs.
This registration process is vital in consumer protection, reducing the likelihood of provider failure and misuse of client funds. The Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA) uses this framework to implement Treating Customers Fairly (TCF) measures. These measures ensure equitable treatment of clients across the South African financial sector. Explore this topic further. The TCF principles translate abstract regulations into tangible benefits for clients, ensuring fair treatment and transparency.
The Role of the FSCA
The FSCA plays a crucial role in this consumer protection framework. They proactively monitor FSP conduct, investigate complaints, and take disciplinary action against providers who violate regulations.
This proactive approach helps maintain high industry standards and provides recourse for consumers who experience unfair treatment.
Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
When things go wrong, the FSP system offers robust complaint and dispute resolution mechanisms. Clients can lodge complaints with the FSCA, who will investigate the matter and facilitate a resolution.
This provides a clear pathway for consumers to seek redress and ensures accountability within the financial services sector. It offers valuable protection for South Africans engaging with these providers.
Verifying an FSP's Legitimacy
Before entrusting your finances to a provider, verify their legitimacy and track record using the FSCA's online resources. This empowers consumers to make informed decisions and avoid potential scams.
By understanding how to use the FSP system effectively, South Africans can protect their financial well-being and participate confidently in the financial marketplace. This transparency allows consumers to hold providers accountable and make informed choices. Active participation is key to maximizing the benefits of the FSP registration system.
FSP Number Verification: Essential Tools and Practical Steps
Knowing how to verify an FSP number is critical for South African consumers making financial decisions. The Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA) provides online tools and databases for instantly checking the legitimacy and status of any financial services provider. However, these resources are only effective if used correctly. This guide will walk you through the verification process, highlighting key steps and important considerations.
How to Verify an FSP Number
The FSCA's online search portal is your primary tool. Here’s a breakdown of how to use it:
Search by FSP Number: Enter the FSP number into the search field and review the results. This quickly confirms if the number is valid and provides details about the provider.
Search by Provider Name: If you don't have the FSP number, you can search by the provider's name. Double-check the returned FSP number against any documentation you have from the provider.
Search by Postal Code or Location: This helps locate FSPs in your area, useful when researching local financial advisors or comparing services.
Search by Individual Representative Details: Verify the credentials of a specific financial advisor. This ensures the individual is authorized to provide services under a valid FSP.
Interpreting Search Results
Understanding the returned information is crucial. Pay close attention to these details:
Registration Status: Ensure the FSP is currently registered and authorized to provide financial services.
Contact Details: Confirm the provider’s address and contact information match what you have. Discrepancies could indicate a problem.
Authorized Services: Verify the FSP is licensed for the specific financial services you need.
History of Complaints or Disciplinary Actions: The FSCA database may reveal past issues, valuable for assessing the provider's track record.
Additional Due Diligence Steps
While the FSCA search is a powerful tool, consider these additional steps:
Online Reviews and Testimonials: Search for independent reviews from other clients for insights into their experiences.
Referrals: Ask friends, family, or colleagues for recommendations. Trusted sources can offer reliable insights.
Direct Contact: Contact the FSP directly with questions about their services, qualifications, and compliance procedures.
Reporting Concerns to the FSCA
Report any discrepancies or concerns about an FSP to the FSCA immediately. They can investigate potential violations and take appropriate action.
By diligently using these verification tools and staying informed, you can reduce your risk and navigate South Africa's financial world confidently. This proactive approach empowers you to make sound financial decisions. Regularly monitoring your provider's status helps safeguard your financial well-being. This ongoing vigilance is crucial in today’s financial environment.
Evolution of FSP Regulation: Technology and Emerging Trends
The financial services landscape in South Africa is constantly changing. FSP regulation must adapt to keep up with these changes. Technology plays a significant role in this evolution, influencing how FSP numbers are issued, monitored, and utilized. This raises a key question: how are these emerging trends shaping the future of financial services in South Africa?
Fintech's Impact on FSP Regulation
Financial technology (Fintech) innovations are disrupting traditional financial service models. This disruption is prompting regulatory adjustments. The Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA) is modernizing its oversight to accommodate digital service delivery and new technologies. This modernization affects how FSP numbers are managed, ensuring the system stays relevant and effective.
Online platforms and mobile applications are becoming more common ways to deliver financial services. This requires new regulatory approaches to address the unique challenges and opportunities these platforms present. This shift necessitates updates to current regulations and the potential creation of new rules to cover these evolving service delivery methods.
The Role of Regulatory Technology (RegTech)
RegTech is streamlining FSP compliance and oversight. These technologies automate compliance tasks, analyze data for potential risks, and improve transparency for both providers and consumers.
Automated reporting tools, for instance, can simplify the annual renewal process for FSP licenses. This reduces the administrative burden on providers and allows the FSCA to process renewals more efficiently. This efficiency benefits both the regulatory body and the FSPs. These advancements also make it easier for consumers to access information about registered providers.
Adapting to a Digital Future
The shift toward digital financial services has significant implications for traditional FSP business models. FSPs must adapt to the rising demand for online services, mobile accessibility, and integrated digital solutions.
These changes require investments in new technologies and staff training to maintain competitiveness and satisfy evolving client expectations. Cybersecurity and data privacy are critical concerns. FSPs must implement robust security measures to protect sensitive client data. This includes complying with relevant legislation like the Protection of Personal Information Act (POPIA), adding another layer of complexity to FSP compliance.
Future of FSP Regulation in South Africa
The FSCA is actively researching international best practices and anticipating future regulatory needs. Their goals are to improve transparency, protect consumers, and encourage innovation within a secure regulatory environment.
This proactive approach is essential for South Africa to stay competitive globally and give consumers access to the newest financial service advancements. This commitment to continuous improvement shows the FSCA's dedication to maintaining a robust and relevant FSP framework that supports innovation and consumer protection.
For South African businesses dealing with these complexities, Zaro provides a streamlined and affordable solution for cross-border payments. Discover how Zaro simplifies international transactions.
